Building a truly smart home often starts with a central brain, a device that brings all your connected gadgets together. This central controller is commonly known as a smart home hub. It acts as a translator, allowing disparate devices to communicate, automate, and respond to your commands.
Before investing in any hardware, it is essential to plan your smart home strategy to ensure long-term compatibility between your chosen devices.
Many homeowners question if they truly need a smart home hub. This guide answers that question, explaining why these devices are pivotal for advanced automation and seamless integration. You will learn about the different types of hubs, how they work, and what features matter most for your home.

Why You Need a Smart Home Hub: The Central Controller Advantage
Imagine your smart lights, smart thermostat, door locks, and security cameras all operating independently. Each device would require its own app, creating a fragmented and frustrating experience. This scenario highlights a significant reason why you need a smart home hub.
A smart home hub serves as a central controller, bringing these devices together under one roof. It creates a unified system where your devices can communicate with each other, even if they use different wireless technologies. This eliminates the need to jump between multiple apps for basic control.
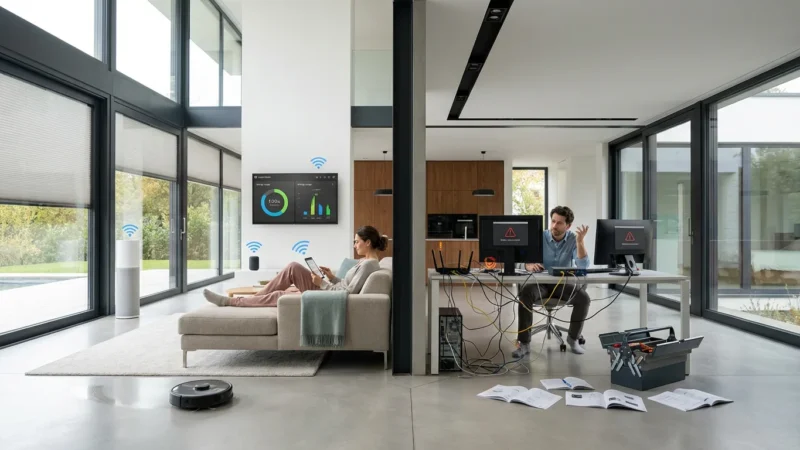
The primary benefit of a hub is enabling sophisticated automations. You can set up complex routines, like your lights gradually dimming as your smart TV turns on for movie night. Another example is your smart thermostat adjusting the temperature automatically when your smart door lock registers your departure.
Many smart home enthusiasts consider a hub essential for a truly integrated and responsive home. It optimizes communication, reduces latency, and unlocks advanced scenarios that simple app-to-device connections cannot achieve. This foundational element ensures your smart home works efficiently for you.
The true power of a smart home emerges when your devices work together seamlessly without constant intervention. A well-chosen smart home hub makes this automation a reality.

Understanding Smart Home Protocols: The Language Your Devices Speak
Smart home devices communicate using various wireless protocols, much like different languages. Your smart home hub acts as a universal translator, enabling devices speaking different “languages” to understand each other. Understanding these protocols helps you select the right hub and devices for your ecosystem.
The most common protocols include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and the emerging Matter standard. Each offers distinct advantages in terms of range, power consumption, and reliability. A robust smart home hub supports multiple protocols, offering greater flexibility and compatibility.
Wi-Fi
Most smart devices initially relied on Wi-Fi due to its ubiquitous presence in homes. Wi-Fi offers high bandwidth and strong data rates, making it suitable for streaming video from security cameras. However, it consumes more power and can quickly overcrowd your home network if you have many devices.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is ideal for short-range, direct connections between two devices, like your smartphone and a smart lock. It uses less power than Wi-Fi, which benefits battery-powered devices. However, its limited range and point-to-point nature restrict its use as a primary network for an entire smart home.
Zigbee and Z-Wave
These two protocols are specifically designed for smart home networks. They create mesh networks, meaning each device can relay signals to other devices, extending the network’s range and reliability. This makes them highly efficient for controlling many devices across a larger home.
- Zigbee: Operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency, similar to Wi-Fi. It’s known for its speed and broad device compatibility across brands. Many smart lighting systems, like Philips Hue, use Zigbee.
- Z-Wave: Utilizes lower frequencies (908.42 MHz in the US), which allows signals to travel further and penetrate walls more effectively. Z-Wave devices often have excellent interoperability, ensuring devices from different manufacturers work together.
Matter
Matter is a new, open-source connectivity standard designed to simplify the smart home landscape. It aims to make devices from different brands work together seamlessly, regardless of their underlying protocol. Matter builds on existing technologies like Wi-Fi, Thread (a mesh networking protocol), and Ethernet.
Matter promises universal compatibility, enhanced local control, and robust security. It represents a significant step towards a truly interoperable smart home, where you choose devices based on features, not just brand compatibility. You can learn more about this initiative on the CSA-IoT website, the organization behind the Matter standard.
Key Features to Look for in a Smart Home Hub
Choosing the right smart home hub involves more than just picking a popular brand. You must consider several key features that dictate its performance, compatibility, and usability in your home. Prioritize what matters most for your specific needs and existing smart devices.
Protocol Support
Ensure the hub supports the protocols used by your current and future devices. A multi-protocol hub supporting Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, and Thread offers the greatest flexibility. This prevents you from being locked into a single ecosystem or requiring multiple hubs.
Ecosystem Compatibility
Does the hub integrate with your preferred smart assistant, such as Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit? Seamless voice control is a major convenience feature for many users. Verify that your chosen hub plays well with your existing ecosystem.
Automation Capabilities
Look for a hub that offers robust and intuitive automation tools. You want to create custom rules, schedules, and scenes without complex coding. Advanced hubs allow for conditional logic, such as “If motion is detected AND it’s after sunset, THEN turn on the lights.”
Local Processing vs. Cloud Processing
Some hubs process commands locally, meaning automations run even without an internet connection. Others rely on cloud processing, which can introduce latency and cease functioning during internet outages. Local processing offers greater reliability and often better privacy.
Ease of Setup and Use
A smart home hub should be easy to set up and manage. Look for hubs with user-friendly apps, clear instructions, and intuitive interfaces. A complex setup can quickly deter beginners from embracing smart home technology.
Expandability and Future-Proofing
Consider the hub’s ability to grow with your smart home. Does it support future standards like Matter? Can it handle a large number of devices without performance degradation? Investing in a hub that supports emerging technologies ensures longevity.

Top Smart Home Hubs Compared: Finding Your Best Match for 2025
The market offers several excellent smart home hubs, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the best smart home hubs 2025 means evaluating your priorities: budget, ease of use, device compatibility, and desired level of automation. Here is a comparison of leading options.
Samsung SmartThings Hub
SmartThings remains a popular choice for its broad compatibility and extensive device support. It handles Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi devices, acting as a true central controller. You can connect everything from smart lights and sensors to thermostats and door locks.
- Pros: Excellent device compatibility, supports many protocols, robust automation engine, strong community support.
- Cons: App interface can be complex for beginners, relies on cloud processing for some automations.
- Best For: Users with a diverse range of smart devices from various manufacturers seeking powerful automation.
Hubitat Elevation Hub
The Hubitat Elevation stands out for its strong emphasis on local processing, which ensures reliability and responsiveness even without an internet connection. It supports Zigbee and Z-Wave, making it a favorite among privacy-conscious and advanced users.
- Pros: Local processing for speed and reliability, strong privacy features, advanced automation capabilities.
- Cons: Steeper learning curve for beginners, less sleek interface than competitors, primarily for Zigbee/Z-Wave.
- Best For: Tech-savvy users prioritizing privacy, local control, and advanced custom automations.
Aeotec Smart Home Hub (SmartThings compatible)
This hub is the current generation of Samsung SmartThings hardware, manufactured by Aeotec. It offers the same core functionality as previous SmartThings hubs, including Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi support. It integrates seamlessly with the SmartThings ecosystem and app.
- Pros: Modern hardware, comprehensive protocol support, leverages the mature SmartThings platform.
- Cons: Still shares SmartThings’ reliance on cloud for some functions, requires a SmartThings account.
- Best For: New SmartThings users or those upgrading older SmartThings hardware, desiring broad compatibility.
Amazon Echo Devices (with built-in hub)
Some Amazon Echo devices, such as the Echo Show 10 and Echo Studio, include a built-in Zigbee hub. This allows them to directly control Zigbee devices without a separate hub. They also support Wi-Fi devices and act as a central voice controller for your smart home.
- Pros: Combines smart speaker functionality with a hub, simple setup for Zigbee devices, integrated Alexa voice control.
- Cons: Limited to Zigbee and Wi-Fi protocols, automation capabilities are less advanced than dedicated hubs.
- Best For: Beginners who want a simple entry into smart home automation, primarily using Zigbee lights and sensors.
Apple HomePod Mini / Apple TV (HomeKit Hubs)
Apple HomePod Mini and Apple TV devices serve as HomeKit hubs, enabling remote access to your HomeKit devices and running automations. The HomePod Mini also acts as a Thread border router, supporting new Matter-over-Thread devices. These devices offer a robust and secure ecosystem for Apple users.
- Pros: Seamless integration with Apple ecosystem, strong focus on privacy and security, supports Matter-over-Thread.
- Cons: Primarily for HomeKit-compatible devices, often more expensive hardware.
- Best For: Apple users deeply invested in the HomeKit ecosystem who prioritize privacy and ease of use.
According to Wirecutter’s smart home guides, dedicated hubs often provide more robust and reliable control over a wider array of devices compared to smart speakers with integrated hub functionality.

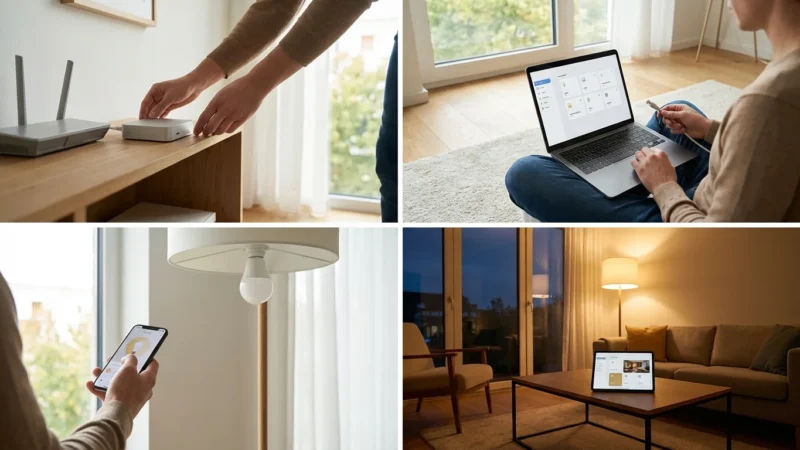
Setting Up Your Smart Home Hub: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up your smart home hub might seem daunting, but it follows a straightforward process. Carefully follow these steps to integrate your central controller into your home network. You will soon enjoy enhanced control and automation.
- Unbox and Connect: Remove your hub from its packaging. Plug the power adapter into an outlet and connect the Ethernet cable to your router if your hub requires a wired connection. Many modern hubs connect via Wi-Fi.
- Download the App: Download the dedicated app for your smart home hub from your smartphone’s app store. This app guides you through the setup process and serves as your primary control interface.
- Create an Account: Open the app and follow the prompts to create a user account. This typically involves providing an email address and creating a password. Remember to use a strong, unique password for security.
- Discover the Hub: The app will prompt you to discover your new hub. Ensure your smartphone is on the same Wi-Fi network as your hub. The app will guide you through connecting the hub to your home network.
- Pair Your Devices: Once the hub is online, you can start pairing your smart devices. For Zigbee or Z-Wave devices, put the device into pairing mode, then initiate a device search within your hub’s app. For Wi-Fi devices, you might connect them to the hub indirectly via cloud services or directly if the hub has Wi-Fi control.
- Organize and Name: As you add devices, assign them to rooms and give them descriptive names. This makes voice control and automation much easier. For example, “Living Room Lamp” is more useful than “Device 1.”
- Start Automating: Begin creating your first automations. Start with simple rules, like “Turn on the porch light at sunset.” Gradually build up to more complex routines as you become comfortable with the hub’s capabilities.
Remember, each hub has slightly different setup procedures. Always refer to your hub’s specific instruction manual for detailed guidance. If you encounter issues with electrical devices, always consult a licensed electrician.

Hub-Free Smart Home Options: When Simplicity is Key
While a dedicated smart home hub offers unparalleled integration, it is not always a requirement for every smart home setup. Many users prefer a simpler, hub-free approach, especially when starting with just a few devices. You can still enjoy smart home convenience without a separate central controller.
Most modern smart devices connect directly to your home’s Wi-Fi network. These include smart light bulbs, smart plugs, and even some security cameras. You control these devices through their manufacturer’s app or by linking them to a smart assistant like Alexa or Google Assistant.
Key Characteristics of Hub-Free Setups:
- Direct Wi-Fi Connection: Devices connect directly to your Wi-Fi router, eliminating the need for an additional piece of hardware.
- Manufacturer Apps: You manage each device through its own dedicated app, such as the Philips Hue app (if using Wi-Fi bulbs) or the Kasa app for TP-Link devices.
- Smart Assistant Integration: Alexa, Google Assistant, or HomeKit can act as a rudimentary “hub” by linking to various device accounts. This allows for voice control and basic automations across different brands.
- Limited Protocol Support: Hub-free systems primarily rely on Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. They generally do not support Zigbee or Z-Wave devices without a specific bridge or dedicated hub.
A hub-free setup is excellent for those looking for a budget-friendly starting point. If you have only a few smart plugs and a smart speaker, this approach works well. However, as your device count grows, managing multiple apps and limited cross-device automations can become cumbersome. You might find yourself wanting the unified control of a smart home hub.

Maximizing Your Smart Home Hub’s Potential
Once you have your smart home hub set up, you unlock a world of possibilities for automation and convenience. You can move beyond basic on/off commands and create truly intelligent routines that enhance your daily life. Focus on creating automations that genuinely simplify tasks and save energy.
Advanced Automation Strategies:
- Contextual Scenes: Create scenes that adjust multiple devices based on a specific context. A “Good Morning” scene could open blinds, turn on kitchen lights, and start your coffee maker.
- Sensor-Triggered Actions: Use motion sensors, contact sensors, or ambient light sensors to trigger actions. For example, a motion sensor in your bathroom turns on a low light at night.
- Geofencing: Implement location-based automations using your phone’s GPS. Your smart thermostat can adjust to your preferred temperature when you are a certain distance from home. Your lights can turn on automatically as you pull into the driveway.
- Energy Efficiency Routines: Integrate your smart thermostat with door/window sensors. If a window opens, the thermostat can pause heating or cooling to save energy. You can also schedule smart plugs to turn off energy-hogging devices overnight. Information from Energy Star’s resources emphasizes the energy savings possible with smart thermostats.
- Security Enhancements: Link your smart locks, security cameras, and smart lights. If a door unlocks unexpectedly late at night, your hub can flash indoor lights and send you an alert.
Explore your hub’s specific automation engine, often called “routines,” “rules,” or “scenes.” Experiment with different triggers and actions to discover what works best for your household. The more you use your hub, the more you will appreciate its ability to make your home proactive rather than reactive.

The Future of Smart Home Hubs and the Matter Standard
The smart home landscape is constantly evolving, and the introduction of the Matter standard marks a significant shift. Matter promises to unify the fragmented ecosystem, making smart home hubs even more powerful and essential. You will find that Matter-enabled hubs become increasingly central to future home automation.
Matter’s core goal is to enable seamless communication between devices from different brands, eliminating compatibility headaches. Instead of a hub needing to understand dozens of proprietary languages, it will primarily communicate with Matter-certified devices. This simplifies development and enhances the user experience.
Impact on Smart Home Hubs:
- Universal Compatibility: Your Matter-enabled hub will control any Matter-certified device, regardless of the manufacturer. This simplifies device selection and setup.
- Thread Integration: Many Matter devices will use Thread, a mesh networking protocol similar to Zigbee and Z-Wave but IP-based. Hubs that can act as Thread border routers will be crucial for these devices.
- Enhanced Local Control: Matter emphasizes local control, meaning devices can communicate directly with your hub on your local network. This reduces reliance on the cloud, improving speed, reliability, and privacy.
- Simplified Onboarding: Matter’s streamlined pairing process, often using QR codes, will make adding new devices to your hub much easier.
As Matter gains widespread adoption, existing smart home hubs will likely receive firmware updates to support the new standard. New hubs entering the market will feature Matter compatibility out of the box. Investing in a hub that is either already Matter-compatible or slated for an update provides excellent future-proofing for your smart home. This ensures your central controller remains relevant for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a smart home hub if I only have a few smart devices?
You do not necessarily need a dedicated smart home hub if you have only a few Wi-Fi devices and primarily use a smart speaker for control. Many smart devices connect directly to Wi-Fi and can be controlled via their own apps or basic smart assistant integrations. A hub becomes more beneficial as your device count grows and you seek advanced automations.
What is the difference between a smart speaker with a hub and a dedicated smart home hub?
A smart speaker with a built-in hub, like some Amazon Echo models, can directly control certain smart home devices, usually Zigbee. It offers convenience and voice control. A dedicated smart home hub, such as SmartThings or Hubitat, typically supports a wider range of protocols (Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread) and provides more powerful, flexible automation capabilities. Dedicated hubs are designed as the primary central controller.
Can a smart home hub improve my home’s security?
Yes, a smart home hub can significantly improve your home’s security. It integrates devices like smart locks, security cameras, motion sensors, and door/window sensors into a cohesive system. You can create automations such as flashing lights and sending alerts if a sensor detects unusual activity, or automatically locking doors when you leave. Many hubs also offer professional monitoring integration options.
What protocols should my smart home hub support?
For maximum flexibility and future-proofing, your smart home hub should ideally support Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Thread (for Matter compatibility). Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are also common, but often handled by your router or directly by devices. Supporting multiple protocols ensures compatibility with a broad range of devices from various manufacturers, giving you more choices for your smart home.
Are smart home hubs difficult to set up?
No, most modern smart home hubs are designed for relatively easy setup. They typically involve plugging in the device, downloading a companion app, and following on-screen instructions to connect it to your home network. Adding devices is usually a guided process within the app. While advanced automations can have a learning curve, basic setup is straightforward for most users.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Smart home devices involve electrical connections and data privacy. Always follow manufacturer instructions for installation. For complex wiring or HVAC work, consult a licensed professional.
Researching smart home mistakes beginners should avoid can help you navigate the initial configuration without common pitfalls.
If you are looking for an even more powerful, open-source alternative for local control, you might want to learn how to get started with Home Assistant.









Leave a Reply