Your home’s WiFi network serves as the central nervous system for all your smart devices. A robust and well-configured network ensures your smart lights respond instantly, your security cameras stream reliably, and your smart thermostat maintains comfortable temperatures without interruption. Without a strong foundation, even the most advanced smart home gadgets deliver a frustrating experience. This guide empowers you to optimize your WiFi setup, providing a seamless and efficient smart home environment.

Understanding Your Smart Home’s Network Foundation
Every smart home relies on a stable and fast internet connection, with WiFi acting as the primary conduit for most devices. Understanding how your WiFi setup functions is the first step to building an efficient smart home. Your router broadcasts wireless signals, allowing devices to connect and communicate with each other and the internet.
Many smart devices use WiFi directly, connecting to your network just like your smartphone or laptop. Others, such as those employing Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Matter protocols, require a hub that connects to your WiFi, bridging these different communication standards. For a deep dive into connectivity options, you can explore resources like The Verge’s smart home guides.
Key WiFi Terms You Should Know
You encounter specific terms when discussing WiFi setup and network optimization. Knowing these helps you make informed decisions for your smart home.
- Router: This device connects your home network to the internet and broadcasts your WiFi signal. It acts as the traffic controller for all your connected devices.
- Modem: The modem connects your home to your Internet Service Provider (ISP), converting internet signals into a format your router understands. Many ISPs provide combination modem/routers.
- Bandwidth: This refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network connection in a given amount of time. Higher bandwidth allows for more devices and faster speeds.
- Frequency Bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz): These are the radio frequencies your router uses to transmit WiFi signals. Each has distinct characteristics impacting smart device performance.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): This is the name of your WiFi network that appears when you search for available networks. You set this name during your initial WiFi setup.
The Difference Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Most modern routers are dual-band, meaning they broadcast signals on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Each band offers advantages and disadvantages for smart devices. You can configure your best router settings for each band.
- 2.4 GHz Band:
- Pros: Offers a longer range and better penetration through walls and obstacles. Many older smart devices only support 2.4 GHz.
- Cons: Lower maximum speeds and more susceptible to interference from other devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth. It handles fewer devices efficiently.
- 5 GHz Band:
- Pros: Delivers faster speeds and handles more simultaneous connections. It experiences less interference in crowded environments.
- Cons: Has a shorter range and struggles to penetrate walls and floors effectively. Some smart devices, especially simpler ones, do not support 5 GHz.
For your smart home, you will typically connect devices that need high bandwidth and close proximity to the router to 5 GHz. You will assign devices like smart plugs or sensors to the 2.4 GHz band.

Choosing the Right Router for Your Connected Home
Your router is the cornerstone of your smart home, dictating how effectively your devices communicate. Selecting the appropriate hardware prevents many connectivity issues before they start. You need a router capable of handling numerous connections and maintaining consistent speeds across your home.
Router Types for Smart Homes
Selecting underpowered networking hardware is one of the most common smart home mistakes that can lead to connectivity frustration later on.
Consider these options when you select a router for your smart home needs. Each type offers different benefits for your specific WiFi setup.
- Standard Routers: Suitable for smaller homes with fewer smart devices. They offer basic functionality but might struggle with a large number of connections or extensive coverage.
- Mesh WiFi Systems: Ideal for larger homes or those with dead spots. These systems use multiple access points to create a single, unified WiFi network, extending coverage seamlessly. This improves network optimization significantly.
- Gaming Routers: Designed for high performance and low latency, often featuring advanced Quality of Service (QoS) features. While not strictly necessary, they offer excellent performance for bandwidth-intensive smart home tasks like 4K video streaming from security cameras.
Essential Router Features for Smart Devices
When you shop for a new router, prioritize these features to ensure optimal performance for your smart home. These features contribute directly to how to set up WiFi network for smart home effectively.
- WiFi 6 (802.11ax) or WiFi 6E: These newer WiFi standards offer faster speeds, improved efficiency, and better performance in environments with many connected devices. They handle your growing smart home ecosystem more effectively.
- Dual-Band or Tri-Band: Ensure your router supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Tri-band routers add a second 5 GHz band, providing even more capacity for devices.
- Gigabit Ethernet Ports: These allow for fast wired connections to devices like smart home hubs, gaming consoles, or media servers, freeing up wireless bandwidth.
- Strong Processor and RAM: A powerful router can manage more connections and process data more efficiently. Look for routers with a dual-core or quad-core processor.
- Parental Controls and Guest Network: These features enhance security and control. A dedicated guest network keeps your smart devices separate from visitor access.
Consumer Reports often reviews the best routers for various needs, providing valuable insights into performance and reliability. You can check their recommendations when making a purchase.
Optimizing Router Placement for Maximum Coverage
The physical location of your router dramatically affects your WiFi signal strength and coverage. Proper placement ensures every corner of your home receives a reliable signal, allowing your smart devices to perform optimally. This crucial step impacts your overall WiFi setup.
Strategic Placement Tips
Once you have verified your coverage, you can confidently begin installing the best first smart home devices for your new network.
Follow these guidelines to find the best location for your router. This contributes to solid network optimization across your entire property.
- Central Location: Position your router in the most central location possible in your home. This distributes the signal evenly in all directions. Avoid placing it in a corner or against an exterior wall.
- Elevated Position: Place your router on a high shelf or on top of furniture, rather than on the floor. WiFi signals spread outwards and slightly downwards, so an elevated position helps them broadcast over obstacles.
- Away from Obstructions: Keep your router away from large metal objects, thick concrete walls, or appliances that emit electromagnetic waves. These include microwaves, refrigerators, and washing machines, which can interfere with the signal.
- Minimize Interference: Place your router away from other wireless electronics, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and Bluetooth speakers. These devices operate on similar frequencies and can cause signal degradation.
- Consider Signal Extenders or Mesh Systems: If you have a large home or multiple floors, a single router may not be sufficient. WiFi extenders or a mesh WiFi system can boost your signal and eliminate dead zones, providing comprehensive coverage for all your smart devices.
Think of your WiFi signal like a light bulb: it emits light in all directions, but walls and large objects cast shadows. Your goal is to minimize those shadows for your WiFi setup.

Essential Router Settings for Smart Device Performance
Beyond placement, configuring your router’s internal settings significantly improves the performance of your smart home. Access your router’s administration page, usually by typing its IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into a web browser. Consult your router’s manual for specific instructions and the default login credentials. These are the best router settings for smart devices.
Update Your Router’s Firmware
Firmware is the operating system for your router. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve performance, patch security vulnerabilities, and add new features. Regularly updating your router’s firmware is a simple yet critical step for network optimization.
- Check for Updates: Log into your router’s administration interface. Look for a section labeled “Firmware Update,” “System Update,” or “Maintenance.”
- Initiate Update: Follow the on-screen prompts to download and install the latest firmware. This process may involve a router reboot.
- Automate (if available): Some newer routers offer automatic firmware updates, which simplify maintenance. Enable this feature if your router supports it.
Secure Your Network
Network security is paramount. An unsecured network leaves your smart devices vulnerable to unauthorized access and potential privacy breaches.
- Change Default Login Credentials: The very first step is to change the default username and password for your router’s administration page. Use a strong, unique password.
- Use WPA3 or WPA2 Encryption: Ensure your WiFi network uses WPA3 or WPA2-PSK (AES) encryption. WPA3 offers the strongest security, but WPA2 is still robust and widely compatible. Avoid WEP or WPA/WPA2-TKIP, as these are less secure.
- Strong SSID and Password: Choose a unique and complex password for your WiFi network itself. Make it long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable a Guest Network: Set up a separate guest network for visitors. This isolates them from your main network where your smart devices reside, preventing potential security risks.
Optimize WiFi Channels
Wireless channels are frequency subdivisions that your router uses to transmit data. If multiple networks in your area use the same channel, interference occurs, slowing down your network.
- Use a WiFi Analyzer App: Download a WiFi analyzer app on your smartphone or computer. These apps show you which channels are most congested in your area.
- Select Less Crowded Channels: In your router’s settings, navigate to the WiFi settings for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Manually select a less congested channel. For 2.4 GHz, channels 1, 6, and 11 are non-overlapping; try one of these if they are clear. For 5 GHz, there are more non-overlapping channels available.
- Enable Auto Channel Selection: If you are unsure, many routers have an “Auto” channel selection feature, which automatically chooses the best channel. This works well for many users, but manual selection often yields better results in congested areas.
Implement Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS settings allow you to prioritize certain types of network traffic. This is invaluable in a smart home, ensuring critical devices receive the bandwidth they need. For instance, you can prioritize your smart security cameras or video doorbell.
- Access QoS Settings: Look for a “QoS” or “Traffic Prioritization” section in your router’s interface.
- Prioritize Critical Devices: Identify your most important smart devices (e.g., security cameras, smart speakers for emergencies). Set them to high priority.
- Prioritize Traffic Types: Some routers allow you to prioritize types of traffic, such as video streaming, online gaming, or VoIP calls. Prioritize video traffic if you have many streaming smart devices.
Consider Band Steering
Band steering is a feature that automatically directs devices to the optimal WiFi band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) based on their capabilities and signal strength. This can improve overall network efficiency and ensures how to set up WiFi network for smart home runs smoothly.
“The best smart home is the one you don’t have to manage. Your network should fade into the background, working flawlessly.”

Managing Your Smart Home Network: Best Practices
Even with the best initial WiFi setup, ongoing management ensures your smart home runs smoothly. Proactive measures keep your network optimized and secure. These practices are crucial for long-term network optimization.
Regular Network Audits
Effective management also involves setting up a smart home app to centralize the control of your various connected devices.
Periodically review the devices connected to your network. This helps you identify unfamiliar devices and ensures only authorized gadgets consume your bandwidth.
- Check Connected Devices: Log into your router’s interface to view a list of all connected devices. Most routers display the device name, IP address, and MAC address.
- Remove Unrecognized Devices: If you find an unfamiliar device, investigate it. If it is truly unauthorized, you can block its access via your router settings.
- Update Device Firmware: Just like your router, individual smart devices also receive firmware updates. Regularly check for and apply updates to improve security and performance.
Separate Smart Devices with a Dedicated Network
For advanced users, creating a separate WiFi network for your smart devices offers enhanced security and performance. This is particularly useful if you have many IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
- Use Your Router’s Guest Network: Configure your router’s guest network specifically for your smart devices. Ensure it is isolated from your main network.
- Implement VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): More advanced routers or managed switches allow you to create VLANs. This provides strong network segmentation, giving your smart devices their own virtual network.
- Benefits: This separation prevents smart devices from accessing sensitive data on your main computers or phones. It also ensures that if one smart device is compromised, the threat does not spread to your entire network.
Power Cycling Your Router
Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve many network issues. Think of it as restarting your computer when it acts up.
- Unplug the Router: Disconnect your router’s power cable from the electrical outlet.
- Wait 30 Seconds: Allow the router to completely power down and clear its cache.
- Plug Back In: Reconnect the power cable and wait a few minutes for the router to fully boot up and re-establish your network connection.
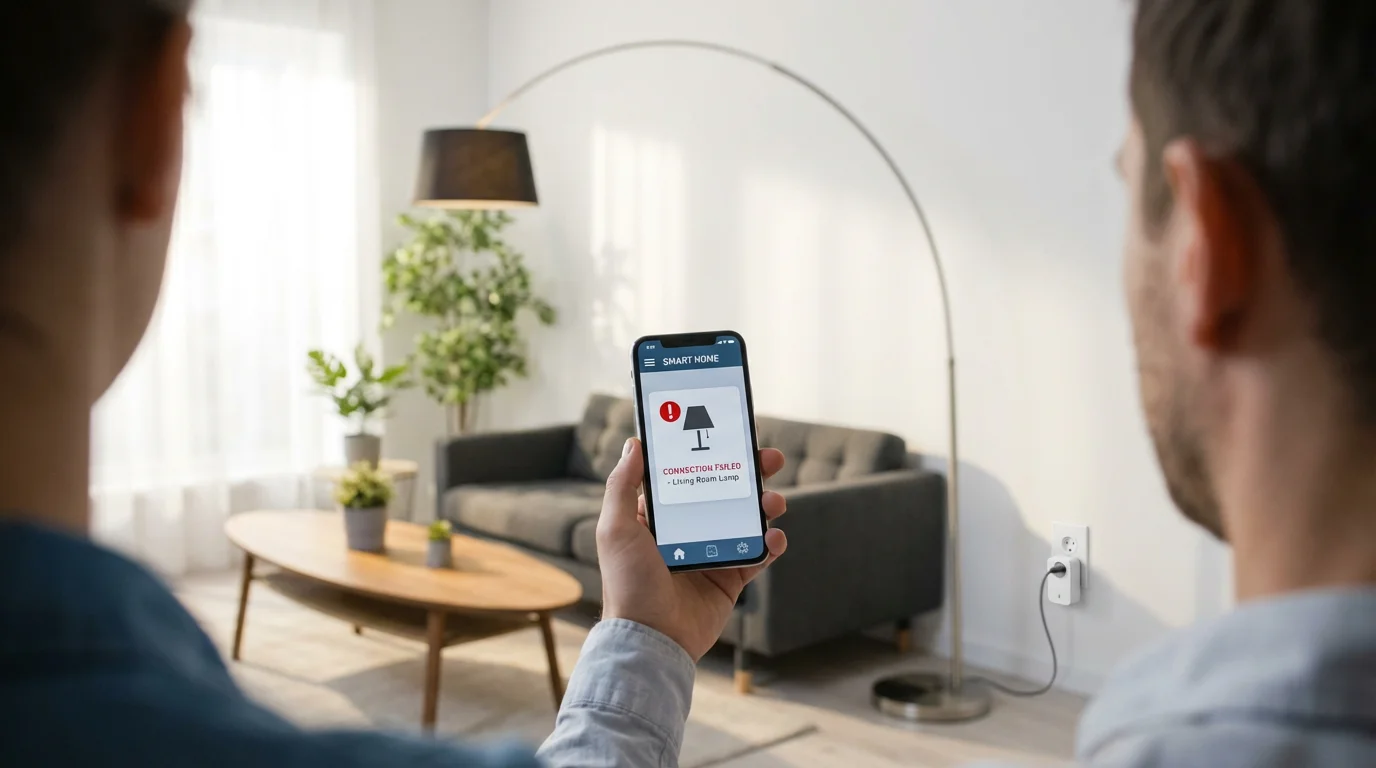

Troubleshooting Common WiFi Issues for Smart Devices
Even with a well-planned WiFi setup, you may occasionally encounter connectivity problems with your smart devices. Knowing how to diagnose and address these issues saves you time and frustration. This section outlines common problems and their solutions for your WiFi setup.
Device Not Connecting to WiFi
This is a frequent issue, especially with new smart device installations.
- Verify WiFi Password: Double-check that you are entering the correct WiFi password. Typographical errors are common.
- Check WiFi Band Compatibility: Many older or simpler smart devices only support the 2.4 GHz band. Ensure your router is broadcasting a 2.4 GHz signal and that your device is attempting to connect to it.
- Proximity to Router: Bring the smart device closer to the router during the initial setup process. Once connected, you can sometimes move it back to its intended location.
- Router Reboot: Perform a power cycle of your router, as described in the previous section.
- Factory Reset Device: As a last resort, factory reset the smart device and attempt the setup process again. Refer to the device’s manual for specific reset instructions.
Frequent Disconnections or Slow Performance
When your smart devices consistently drop offline or respond slowly, your network may be experiencing congestion or interference.
- Check for Interference: Use a WiFi analyzer app to identify congested channels and adjust your router’s WiFi channel settings. Move your router away from potential interference sources like microwaves.
- Reduce Network Congestion: If too many devices are on one band, move some to the other band (e.g., move laptops to 5 GHz, leaving more room on 2.4 GHz for smart plugs). Consider upgrading to a mesh system if your current router is overloaded.
- Router Overload: Your router might be struggling to handle the number of connected devices. A router with a more powerful processor and more RAM can help.
- Firmware Update: Ensure both your router and the problematic smart device have the latest firmware installed.
Range Issues and Dead Zones
If certain areas of your home lack WiFi coverage, your smart devices in those areas will suffer.
- Relocate Router: Re-evaluate your router’s placement. A more central or elevated position can make a significant difference.
- Add a Mesh Node or Extender: Invest in a mesh WiFi system or a WiFi extender to expand your network’s coverage. For larger homes, mesh systems often provide a more seamless experience than traditional extenders. PCMag frequently reviews range extenders and mesh systems, which can help guide your decision.
- Check Antenna Orientation: If your router has external antennas, try adjusting their angles to optimize signal direction. Some suggest pointing them in different directions for better omnidirectional coverage.

Future-Proofing Your Smart Home Network
Technology evolves rapidly. To ensure your smart home remains functional and efficient for years to come, consider future-proofing your network today. This forward-thinking approach to your WiFi setup helps with long-term network optimization.
Embrace New Standards
Invest in hardware that supports the latest WiFi standards.
- WiFi 6 (802.11ax) and WiFi 6E: These standards offer better performance, efficiency, and capacity for multiple devices. Upgrading your router to WiFi 6 or 6E today positions your network to handle future smart home gadgets.
- Matter Connectivity: Matter is a new open-source connectivity standard designed to unify smart home devices across different ecosystems. As more devices adopt Matter, your network needs to be robust enough to support these integrations. Learn more about the Matter Smart Home Standard on the CSA-IoT website.
Plan for Growth
Your smart home will likely grow over time. Plan your network to accommodate this expansion.
- Scalable Mesh Systems: If you start with a single mesh node, ensure the system is expandable. You can add more nodes as your home grows or you introduce more devices.
- Higher Bandwidth Internet Plan: As you add more streaming devices, security cameras, and other data-intensive gadgets, consider upgrading your internet service plan to a higher bandwidth tier.
- Wired Backhaul: If your mesh system supports it, connect mesh nodes to your main router via Ethernet cables. This “wired backhaul” provides a faster and more reliable connection between nodes, reserving wireless bandwidth for your devices.
Regular Security and Maintenance
Maintain vigilance regarding your network’s security and performance.
- Stay Updated: Consistently update your router’s firmware and the firmware of your smart devices. These updates often include security patches and performance improvements.
- Review Privacy Settings: Periodically review the privacy settings of your smart devices and associated apps. Understand what data they collect and how they use it.
- Backup Your Configuration: After you achieve your ideal router settings for smart devices, back up your router’s configuration. This allows for quick restoration if you ever need to factory reset your router.
By implementing these strategies, you build a resilient, high-performing WiFi setup ready for the smart home of today and tomorrow. Your commitment to a strong network foundation ensures your smart devices work seamlessly, providing the convenience, security, and efficiency you expect.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a modem and a router?
A modem connects your home to the internet service provider’s network, translating internet signals. A router then creates a local network in your home, allowing multiple devices to share that internet connection wirelessly via WiFi or through Ethernet cables. Many ISPs provide combination modem/router devices.
Should I connect all my smart devices to the 2.4 GHz band?
Not necessarily. While many smart devices, especially simpler ones like smart plugs and sensors, use the 2.4 GHz band due to its longer range, devices requiring higher bandwidth or faster response times, such as smart security cameras or video doorbells, often perform better on the 5 GHz band. Check device specifications for optimal performance recommendations.
How many smart devices can my WiFi network handle?
The number of devices your WiFi network can handle depends on your router’s capabilities, internet plan bandwidth, and network congestion. High-end routers and mesh systems can typically handle 50-100+ devices efficiently. Older or basic routers might struggle beyond 15-20 devices, especially with active usage. For smooth network optimization, monitor your router’s performance and consider an upgrade if you experience slowdowns.
Is it safe to enable a guest network for smart devices?
Yes, enabling a separate guest network specifically for your smart devices is a recommended security practice. This isolates your IoT devices from your primary network where your computers and personal data reside. If a smart device is ever compromised, it limits the attacker’s access to the rest of your home network.
What is band steering and should I enable it?
Band steering is a router feature that automatically guides devices to the most appropriate WiFi band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) based on signal strength, congestion, and device capability. Enabling band steering generally improves network efficiency and device performance, ensuring your smart devices connect to the optimal band without manual intervention.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Smart home devices involve electrical connections and data privacy. Always follow manufacturer instructions for installation. For complex wiring or HVAC work, consult a licensed professional.
It is often best to plan your smart home before purchasing equipment to ensure your network can handle the specific devices you intend to install.
If you find some of this technical language confusing, our smart home glossary covers many more terms every beginner should know.









Leave a Reply